
Natural isotopic separation from biological redox processes and the precipitation of organic ammonia or nitric acid cause the relative quantity of 14N and 15N to change in the atmosphere, but not everywhere. 2H, 6Li, 10B, and 180mTa are the other four stable odd–odd nuclides (nuclides with odd protons and neutrons). The CNO cycle in stars produces stable isotopes, although 14N is more abundant because neutron absorption is the rate-limiting phase. The result is an atomic mass of 14.007 u. Properties of Nitrogen trifluoride It has a molar mass of 71. The first is far more prevalent, accounting for 99.634 percent of natural nitrogen, whereas the second (slightly heavier) accounts for the remaining 0.366 percent. NF3 lewis structure has 3 fluorine and 1 nitrogen atom connected with three single bonds. It means when you have one mole of nitrogen, it is equivalent to about 14.01 grams of nitrogen, and it is also equivalent to about 6.02214 1023 nitrogen atoms: 14.01 g N 1 mol N atoms 6. Numerically, this is the molar mass of nitrogen. The stable isotopes of nitrogen are 14N and 15N. Using a periodic table, we can find that nitrogen has an atomic mass of about 14.01 amu. Nitrogen has an atomic mass of 14.01 amu or 14.01 g/mol. The molar mass of a substance is defined as the mass of 1 mol of that substance, expressed in grams per mole, and is equal to the mass of 6. Because electrons have a very low mass compared to protons or neutrons, their mass has no bearing on the calculation. The total masses of neutrons, protons, and electrons in an atom are atomic masses.
The nitrogen cycle explains how nitrogen moves from the atmosphere to the ecosystem and organic molecules before returning to the atmosphere.

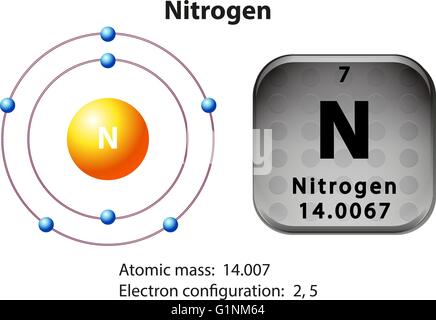
The human body requires approximately 3% of nitrogen via mass. N is found in all animals, particularly in amino acid residues, nucleic acids, and the energy transportation component of adenosine triphosphate. The most common uncombined element, N 2, makes up 78 % of the Earth’s environment. It is a standard element across the universe, well with the Milky Way and the rest of the universe having the sixth-highest overall abundance.Īt room temperature or pressure, two or more chemical atoms combine to form N 2, odorless and colorless diatomic gas. N is a nonmetal that belongs to Periodic Group 15, which is also referred to as pnictogens. The chlorine atom nitrogen has the atomic number of 7, and the symbol is N.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
